Last Updated on May 24, 2024
In a world fixated on happiness, what occurs when that emotion becomes elusive, akin to a forgotten language? Enter Unipolar Depression, where clouds obscure the sun, dimming even the brightest moments.
Depression is a prevalent mental health issue characterized by symptoms that vary in intensity from mild to severe. Approximately 8.3% of adults in the United States have experienced some form of depression at some stage in their lives. This blog is focuses on “What is Unipolar Depression?”
Unipolar Depression, also known as Major Depressive Disorder (MDD), is a mental health condition characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, emptiness, or hopelessness. Unlike bipolar depression, which involves both depressive and manic episodes, this condition involves only depressive episodes. Symptoms can vary widely but may include changes in sleep patterns, appetite, energy levels, concentration, and interest in activities once enjoyed. It can greatly affect daily functioning and overall quality of life.
Read more about the different types of Depression: Comparison between Dysthymia vs Major Depression
Many Faces of Unipolar Depression Symptoms
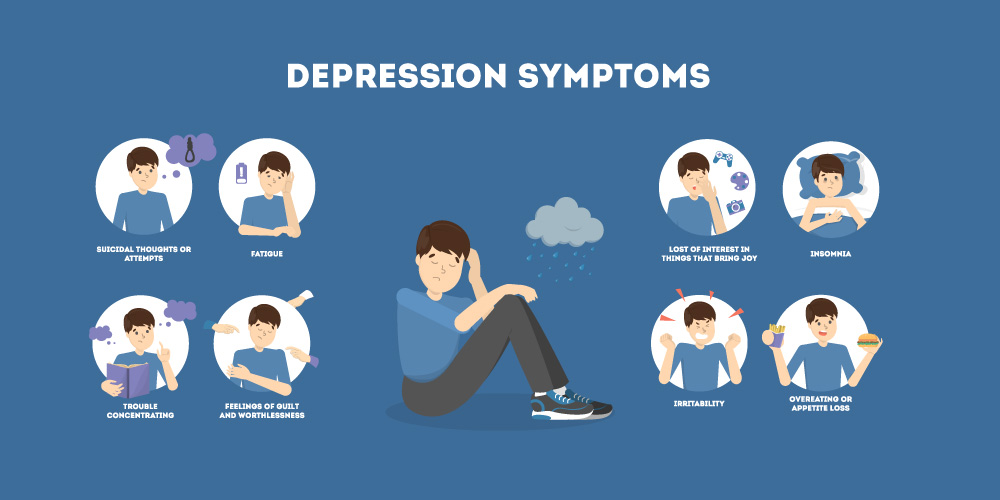
Unipolar Depression can manifest in a variety of ways, making it sometimes difficult to recognize. Below are a few symptoms to recognize this condition:
- Apathy: One may experience a lack of emotional response toward situations, people, and hobbies that were once enjoyable to them.
- Sadness: While not everyone with depression experiences sadness (some may feel angry or irritable), individuals may still feel overwhelmed by profound feelings of sadness, emptiness, or tearfulness.
- Irritability: Individuals may experience irritability, a sense of being “on edge,” or feelings of anger towards things that typically would not provoke such reactions.
- Slowness: If one perceives a reduction in the usual pace of speech, movement, or thought, it could be indicative of major depression.
Thoughts or Plans of Suicide: Persistent thoughts or fantasies of suicide are not typical and require immediate attention. Contact a doctor, go to the emergency room, or seek assistance from a trusted loved one to initiate treatment promptly if this is a primary symptom.
Unipolar Depression vs Bipolar Depression
| Unipolar Depression | Bipolar Depression |
|---|---|
| Characterized by depressive episodes only. | Contains both depressive and manic or hypomanic episodes. |
| Individuals experience persistent feelings of sadness, emptiness, or hopelessness. | Individuals may experience periods of intense euphoria, increased energy, and risky behavior during manic episodes. |
| Symptoms may include changes in sleep patterns, appetite, energy levels, concentration, and interest in activities. | Depressive episodes in Bipolar disorder are like those in Unipolar Depression. |
| Treatment typically involves therapy, medication, lifestyle changes, and support from healthcare professionals. | Treatment often includes mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, antidepressants (with caution), therapy, and lifestyle adjustments. |
You might find this interesting! Navigating Arguments: Bipolar Disorder
Unlocking Hope: Diagnosis and Treatment Strategies for Unipolar Depression
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis of this depression typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist.
- The diagnostic process may include a thorough review of the individual’s medical history, symptoms, and any family history of mental health conditions.
- Mental health assessments, questionnaires, and standardized screening tools may be used to aid in diagnosis.
- The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) criteria are often utilized by clinicians to diagnose this condition, requiring the presence of specific symptoms for a certain duration.
- It is essential for healthcare providers to rule out other potential causes of depressive symptoms, such as medical conditions or substance abuse, before making a diagnosis.
Treatment
- Psychotherapy: Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Interpersonal Therapy (IPT), or Psychodynamic Therapy is often recommended as a first-line treatment. These therapeutic approaches aim to identify and address negative thought patterns, improve coping skills, and enhance interpersonal relationships.
- Antidepressant Medications: Selective-Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs), or Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms and alleviate symptoms. It is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to find the most effective medication and dosage with the fewest side effects.
- Lifestyle Modification: Regular exercise, healthy eating habits, adequate sleep, stress management techniques, and avoidance of alcohol and recreational drugs, can play a crucial role in managing symptoms and promoting overall well-being.
- Clinical Trial: Clinical Trials conducted by the Revive Research Institute offers hope for individuals battling Unipolar Depression or Major Depressive Disorder, delving into potential treatments designed to provide relief and empowerment to those affected by this condition.
- Support from Relationships: Support from family, friends, support groups or mental health professionals can provide valuable encouragement, understanding, and assistance throughout the treatment process.
Takeaway
Unipolar Depression, also known as Major Depressive Disorder, has the potential to impact every facet of an individual’s life, from their relationships and career to their education and self-perception. Misconceptions surrounding depression can hinder someone’s capacity to seek or receive treatment.
It is crucial to recognize the diverse manifestations of this condition and to seek support from healthcare professionals, loved ones, and appropriate resources. By shedding light on the symptoms and pathways to healing, we can offer hope and resilience to those struggling with this condition. Through tailored interventions such as psychotherapy, medication, lifestyle adjustments, and potential treatment from Clinical Trials, individuals can reclaim their sense of joy and vitality, transcending the barriers that once obscured the path to happiness.




