All About Epilepsy
Epilepsy, a neurological disorder marked by recurrent seizures, affects millions worldwide. Among its various forms, nocturnal epilepsy stands out, as it primarily occurs during sleep. Understanding this condition is important for improving the quality of life of those affected and advancing treatment options. According to WHO, more than 70% of epilepsy cases are curable if diagnosed at the right time. Let’s learn about nocturnal seizures, including its prevalence, symptoms, diagnosis, associated conditions like sleep-related hyper motor epilepsy (SHE), potential risks, complications, and treatment options. Drawing on recent studies, it aims to enhance understanding and awareness of this sleep-related disorder.
What is Nocturnal Epilepsy?
Nocturnal epilepsy is a form of epilepsy where seizures exclusively occur during sleep. This type of epilepsy can significantly impact sleep quality and overall health. Unlike other forms of epilepsy that may manifest during waking hours, nocturnal seizures are linked to the brain’s activity during sleep. This condition is particularly intriguing due to its timing and impact on rest. It is essential to differentiate nocturnal seizures from other sleep disorders to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Prevalence And Onset of Age
Prevalence studies indicate that nocturnal epilepsy is less common than other types, but it is often underdiagnosed due to its occurrence during sleep. Age of onset of developing seizures may occur from 1 year old up to 60 years of age. Around 80% of cases were diagnosed before 20 years of age. Recognizing the signs and understanding the nature of this type of epilepsy is essential for diagnosis, effective treatment and management, and improving patient outcomes.
Causes of Nocturnal Epilepsy
- The exact cause remains unclear, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- Common triggers include brain injury, brain infection, stroke, tumor, sleep deprivation, stress, and changes in medication.
- Recognizing these triggers can help manage and reduce the frequency of seizures.
Nocturnal Epilepsy Symptoms
Recognizing nocturnal seizure symptoms can be challenging as they often go unnoticed by the individual experiencing them. Common symptoms include
Motor Symptoms
- Involuntary movements such as jerking, twitching, or stiffening of the limbs.
- Repetitive motions like chewing or swallowing.
- Bedwetting or loss of bladder control.
Autonomic Symptoms
- Changes in heart rate, breathing, and sweating
Cognitive Symptoms
- Confusion, fear, memory loss, and disorientation upon waking
Nocturnal epilepsy symptoms can significantly affect sleep quality, leading to daytime fatigue and other complications. Moreover, this type of epilepsy is often associated with other sleep disorders, such as obstructive sleep apnea. Individuals with nocturnal seizures might experience breathing difficulties during sleep, which can exacerbate both conditions.
Diagnosis Of Nocturnal Epilepsy
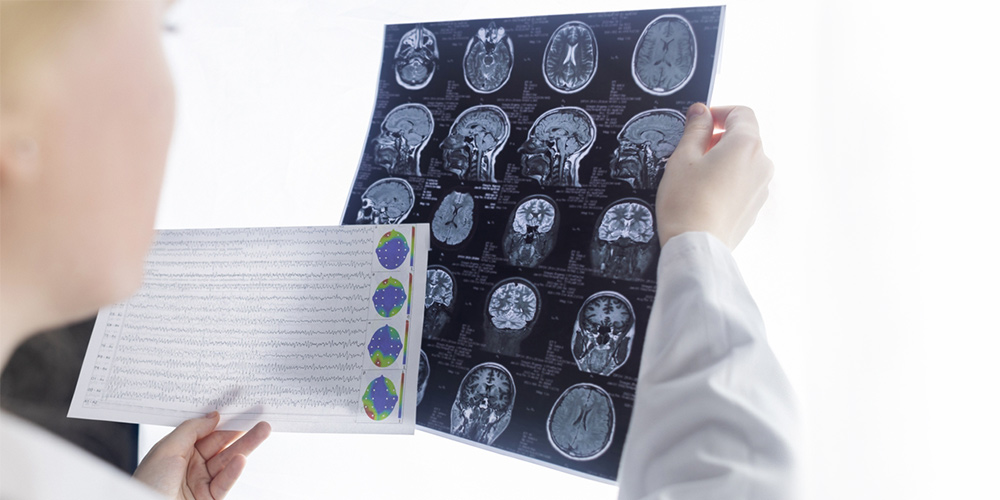
Diagnosing nocturnal seizures requires a thorough evaluation, including medical history, physical examination, and specialized tests. Key diagnostic tools include:
- Electroencephalogram (EEG): Records electrical activity in the brain to detect abnormal patterns.
- Polysomnography: Comprehensive sleep study that monitors brain waves, blood oxygen levels, heart rate, and breathing.
- Video EEG Monitoring: Combines EEG with video recording to capture seizures during sleep.
Associated Conditions
Sleep-Related Hyper motor Epilepsy (SHE)
Sleep-related hyper motor epilepsy (SHE) is a rare form of nocturnal epilepsy characterized by complex motor seizures that occur predominantly during sleep. Understanding SHE can provide insights into the broader spectrum of nocturnal epileptic disorders.
| Condition | Key Features | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|
| Nocturnal Epilepsy | Seizures during sleep, various motor and cognitive symptoms | Up to 20% of epilepsy cases |
| Sleep-Related Hyper motor Epilepsy (SHE) | Complex motor seizures, primarily during sleep | Rare, exact prevalence unknown |
Potential Risks or Complications of Nocturnal Epilepsy
Untreated nocturnal seizures or epilepsy can lead to several complications, including;
- Sleep Disruption: Frequent seizures disrupt normal sleep patterns, leading to chronic sleep deprivation.
- Daytime Fatigue: Poor sleep quality results in excessive daytime sleepiness and impaired cognitive function.
- Injury Risk: Seizures during sleep can cause physical injuries, such as falls or head trauma.
- Comorbid Conditions: Nocturnal epilepsy is often associated with other conditions, such as focal onset epilepsy and obstructive sleep apnea.
Interlinking Studies
Focal Onset Epilepsy
A notable study explored the link between nocturnal epilepsy and focal onset epilepsy. Research indicates that individuals with focal onset epilepsy are at a higher risk of developing nocturnal seizures, indicating a need for comprehensive monitoring and tailored treatment plans.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
The relationship between nocturnal epilepsy and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) has been a significant focus of research. Obstructive sleep apnea, characterized by repeated breathing interruptions during sleep, can exacerbate nocturnal seizures symptoms and complicate its management. These episodes are often linked to poor sleep quality and increased daytime drowsiness.
This interplay highlights the necessity of addressing both conditions simultaneously to enhance patient care.
Living well with Nocturnal Epilepsy
Effective management of nocturnal seizures or epilepsy involves a combination of medical treatment and lifestyle adjustments. Common treatment options include:
- Anti-seizure medications tailored to the individual’s specific seizure patterns
- Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy for those with concurrent obstructive sleep apnea
- Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule and avoiding seizure triggers
Medical supervision is crucial for monitoring the condition and adjusting treatment as needed. Ongoing research and clinical trials, such as those conducted by Revive Research Institute, play a vital role in developing innovative therapies and improving patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Nocturnal epilepsy, while less common than other forms, poses unique challenges due to its occurrence during sleep. Understanding nocturnal seizures or epilepsy symptoms, associated conditions, and available treatments is essential for improving the lives of those affected. If you suspect you or someone you know may have nocturnal epilepsy, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. By staying informed and supporting ongoing research, we can contribute to better diagnosis, management, and ultimately, the well-being of individuals with epilepsy.